Pediatric Elbow Radiology
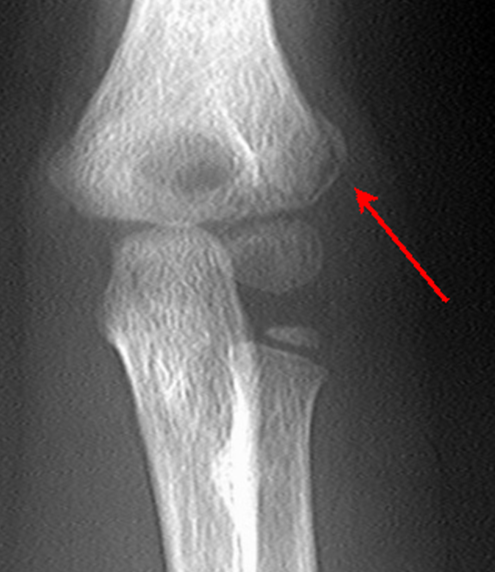
Distal humerus fractures - lateral condylar fracture
- Represent 15% of pediatric elbow injuries.
- The sail sign is usually present along with lateral swelling and edema of the soft tissues.
- It is important to determine if the fracture is displaced or not. Displacement will be posterior and inferior, due to the attachment of the forearm extensor tendons. Displacement occurs when the fracture extends through the articular cartilage of the distal humerus (type IV Salter injury).
- Usually requires open reduction and internal fixation.