PT 861 - The High Risk Infant
Early Care Of The Pre-term Infant
- The first goal of care is to establish adequate ventilation and achieve physiological homeostasis.
- Most pre-term infants, particularly those born very early, require some period of ventilation care, often in combination with surfactant treatment. Ventilation carries several risk factors:
- damage to lung tissue, bronchopulmonary displasia, which can result in chronic lung disease infancy
- difficulty in maintaining an adequate exchange of O2 and CO2, which can result in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- increase in extension positioning of the head, neck and upper trunk which can result in delays in the development of posture control and movement
- Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) ventilation reduces the risk of damage to lung tissues and improves the regulation of O2 and CO2 exchange.
CPAP
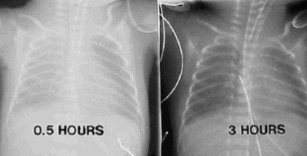
Chest X-ray of neonate on CPAP before and after surfactant treatment.
How would placing the pre-term neonate in prone improve ventilatory capacity?