Equipment tray
 |
Gloves The rescuer should at all times avoid direct contact with the blood and other body fluids of the patient. If available, gloves should be worn during all airway management procedures. |
 |
Suction In most resuscitation situations, the patient will either vomit, or at the very least, have an excess of secretion in their oropharynx. If available, a suction catheter should be included as part of your basic airway equipment. |
 |
Lubricant If a nasopharyngeal airway is used, it will require lubrication of its outer surface prior to insertion. Xylocaine(R) Jelly is used because it is a good lubricant and it reduces irritaion through its local anesthetic effect. |
 |
Nasopharyngeal Airway The nasopharyngeal airway is made of soft, pliable plastic, and is inserted through the nares and into the nasopharynx, thus providing a patent airway to facilitate chest ventilation. It has the advantage of being better tolerated in the conscious or semi-conscious patient than the oropharyngeal airway. It is also easier to insert in a patient who has his/her teeth clenched. It is important to note that the NP airway does not protect the airway from aspiration of vomitus. |
 |
Oropharyngeal Airway The oropharyngeal airway is a rigid plastic device, which is inserted through the mouth into the oropharynx. This provides a patent airway to facilitate chest ventilation. It is important to note that the OP airway does not protect the airway from aspiration of vomitus. |
 |
Bag-Valve Ventilator The bag-valve ventilator is a device designed to ventilate the chest. By attaching an oxygen supply, it can be used to ventilate the chest with a high concentration of oxygen. The bag-valve ventilator can be used with a mask, as in basic airway management, or it can be attached to an endotracheal tube as part of advanced airway management. |
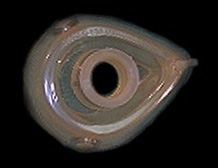 |
Mask Masks are used to provide a tight seal between the patient's face and the bag-valve ventilator. Masks come in various sizes. The correct size of the mask for a particular patient should provide a tight seal around the nose and mouth. The pointed end of the mask creates a seal over the bridge of the patient's nose, while the round end creates a seal between the lower lip and chin. |